Information Security Management - ISO 27001 Tokyo
Cybersecurity defense and risk assessment expertise

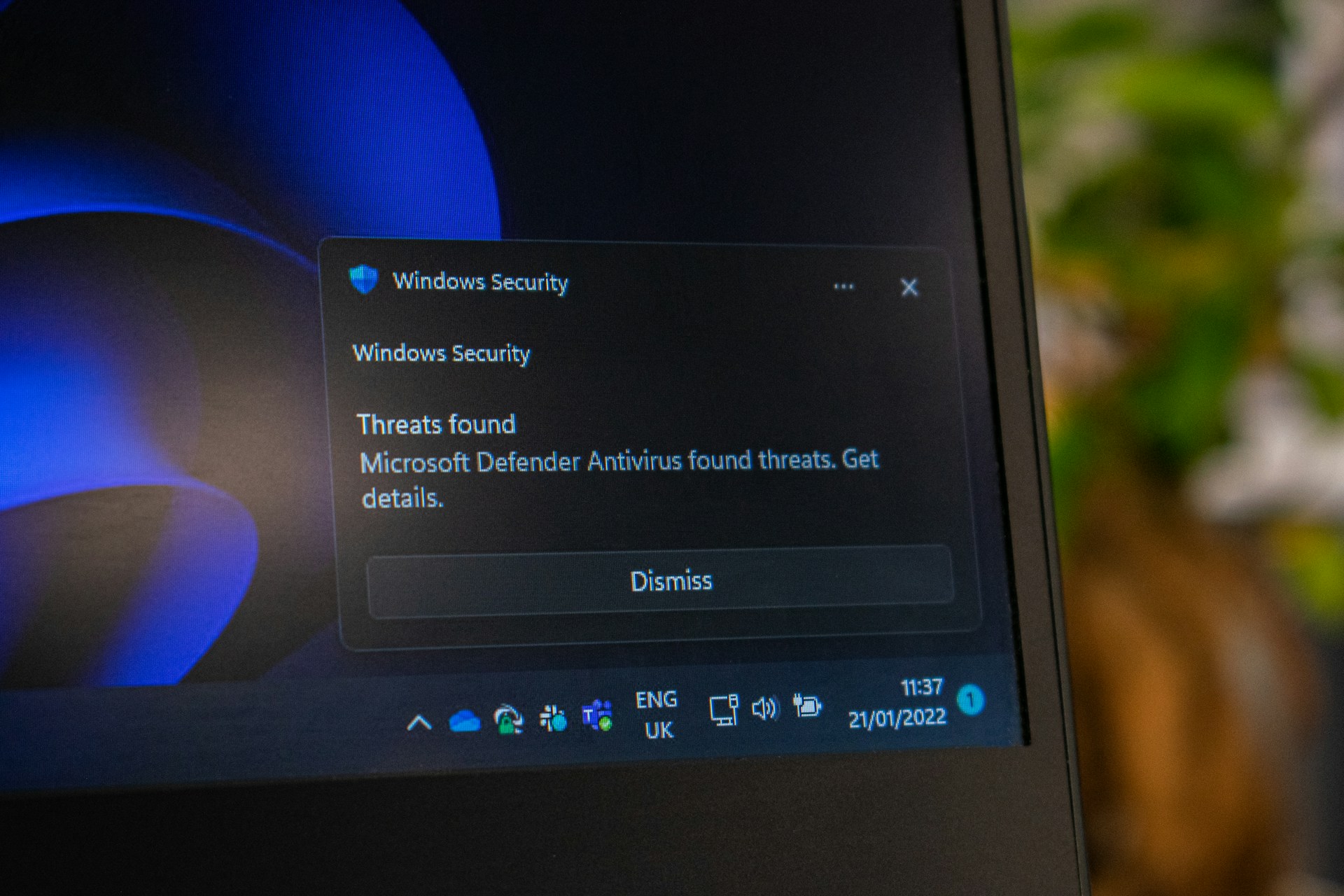






Navigating Japan’s Complex Information Security Landscape
Information security in Japan requires balancing international frameworks like ISO 27001 with unique local regulatory requirements that often confuse international security managers. Unlike many countries where security compliance follows familiar patterns, Japan’s Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA), My Number Act, and J-SOX requirements create a complex regulatory environment that requires specialized local expertise.
Understanding Japan’s Unique Regulatory Framework
Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) Challenges:
Japan’s PIPA differs significantly from GDPR or other international privacy laws that international security teams may understand. While GDPR focuses on individual rights and consent, PIPA emphasizes organizational responsibility and process documentation in ways that require different technical and procedural approaches.
My Number Act Complexity:
The handling of Japan’s individual number system (My Number) creates security requirements that have no equivalent in most other countries. International companies must implement specific technical safeguards, access controls, and audit procedures that go beyond typical data protection measures.
J-SOX IT Controls:
For listed companies, Japan’s version of Sarbanes-Oxley (J-SOX) creates IT control requirements that overlap with but differ from US SOX requirements. Security managers must navigate these differences while maintaining global compliance consistency.
International Company Security Challenges
Global Policy vs. Local Requirements:
International security teams often struggle to reconcile global corporate security policies with Japan’s specific regulatory requirements. This creates a need for security frameworks that satisfy both international corporate standards and local Japanese compliance expectations.
Vendor Ecosystem Navigation:
Japan’s security vendor landscape includes both international players and local specialists with deep regulatory knowledge. International companies need guidance on when to leverage global vendors versus local expertise for optimal compliance and cost effectiveness.
Cultural Security Expectations:
Japanese business culture around information handling, incident response, and privacy expectations differs from Western norms. Security programs must account for these cultural differences to achieve employee buy-in and operational effectiveness.
eSolia’s Bridge Service for International Companies
Regulatory Translation & Integration:
eSolia specializes in helping international companies understand Japan’s security regulatory landscape while maintaining global corporate compliance standards. We translate complex Japanese requirements into familiar international security frameworks, preventing costly compliance gaps.
Comprehensive Approach:
- Dual Compliance Framework: Design security programs that satisfy both Japanese regulatory requirements and international corporate standards
- Cultural Integration: Implement security practices that respect Japanese business culture while meeting global security expectations
- Vendor Navigation: Guide selection between global and local security vendors based on regulatory and operational requirements
- Documentation Bridge: Provide security documentation in formats suitable for both Japanese regulatory compliance and international corporate reporting
ISO 27001 Framework Approach
eSolia’s security consulting follows the ISO 27001 framework, providing a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information. This ensures it remains secure through a risk management process that involves people, processes, and IT systems.
Core ISO 27001 Domains We Address
We help implement and manage all 14 control domains of ISO 27001:
Organizational Controls
- A.5 Information Security Policies - Develop and maintain security policies aligned with business objectives
- A.6 Organization of Information Security - Define roles, responsibilities, and governance structures
- A.7 Human Resource Security - Security considerations for employees throughout their lifecycle
- A.8 Asset Management - Identify, classify, and protect information assets
Technical Controls
- A.9 Access Control - Limit access to information and systems based on business requirements
- A.10 Cryptography - Proper use of encryption to protect information confidentiality and integrity
- A.12 Operations Security - Secure operation of information processing facilities
- A.13 Communications Security - Protection of information in networks and supporting systems
Process Controls
- A.11 Physical and Environmental Security - Prevent unauthorized access to premises and equipment
- A.14 System Acquisition, Development and Maintenance - Security in development and support processes
- A.15 Supplier Relationships - Protection of assets accessible by suppliers
- A.16 Information Security Incident Management - Consistent and effective incident response
Compliance & Continuity
- A.17 Business Continuity Management - Information security continuity in adverse situations
- A.18 Compliance - Avoid breaches of legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations
Risk-Based Security Management
Our approach centers on risk assessment and treatment:
Risk Assessment Process
- Asset Identification - Catalog all information assets and their value
- Threat Analysis - Identify potential threats to each asset
- Vulnerability Assessment - Discover weaknesses that threats could exploit
- Risk Evaluation - Calculate risk levels based on likelihood and impact
- Risk Treatment - Select appropriate controls to mitigate, transfer, or accept risks
- Monitoring & Review - Continuous assessment of risk landscape
Security Implementation Services
Gap Analysis & Planning
- Current state assessment against ISO 27001 requirements
- Maturity level evaluation
- Roadmap development for compliance
- Budget and resource planning
Policy & Procedure Development
- Information security policy framework
- Standard operating procedures
- Incident response playbooks
- Business continuity plans
- Security awareness materials
Technical Implementation
- Security architecture design
- Security controls deployment
- Vulnerability management programs
- Security monitoring solutions
- Data loss prevention strategies
Compliance & Audit Support
- Internal audit programs
- External audit preparation
- Regulatory compliance (GDPR, J-SOX, etc.)
- Third-party risk assessments
- Continuous compliance monitoring
Security Operations Support
Beyond implementation, we provide ongoing security operations support:
- Security Monitoring - Continuous monitoring of security events and alerts
- Incident Response - Rapid response to security incidents with defined escalation procedures
- Vulnerability Management - Regular assessments and remediation tracking
- Security Metrics & Reporting - KPI dashboards and executive reporting
- Security Awareness Training - Regular training programs for all staff levels
Benefits of Our ISO 27001 Approach
- Structured Framework - Systematic approach to security management
- Risk Reduction - Proactive identification and mitigation of security risks
- Compliance Confidence - Meet regulatory and contractual requirements
- Customer Trust - Demonstrate commitment to information security
- Competitive Advantage - ISO 27001 certification as a business differentiator
- Continuous Improvement - Built-in processes for ongoing enhancement
Japan-Specific Considerations
Operating in Japan requires understanding of local requirements:
- Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) compliance
- My Number Act requirements for handling individual numbers
- J-SOX IT controls for listed companies
- Integration with Japanese security vendors (SECOM, ALSOK)
- Bilingual documentation and training materials
- Coordination with Japanese regulatory authorities
Getting Started
Whether you’re beginning your security journey or enhancing existing programs, eSolia provides the expertise to achieve your information security goals. Our consultants hold relevant certifications and continue to expand our expertise through ongoing professional development.
Contact us today to discuss how we can help strengthen your information security posture through ISO 27001-aligned practices.